Joint pain affects people across age groups, especially those with arthritis or long-term degenerative conditions. When discomfort limits movement and reduces quality of life, joint replacement becomes a practical option. The procedure replaces a damaged joint with an artificial one to improve stability and mobility. Growing awareness and better access to orthopaedic care have increased the number of patients opting for Joint replacement in India. The country offers established surgical practices and experienced specialists who manage a wide range of joint conditions. This article outlines the main types of joint replacement surgeries commonly performed and explains how each option supports long-term recovery.
What is Joint Replacement Surgery
Joint replacement aims to restore function when a joint no longer moves smoothly due to wear, injury, or chronic disease. Patients usually consider replacement when pain becomes persistent, daily activities become difficult, and non-surgical treatments fail to help. The artificial joint, often made of metal or high-grade plastic, supports movement and reduces discomfort.
Major Types of Joint Replacement Surgeries in India
To better understand this, here are the most common procedures carried out across the country.
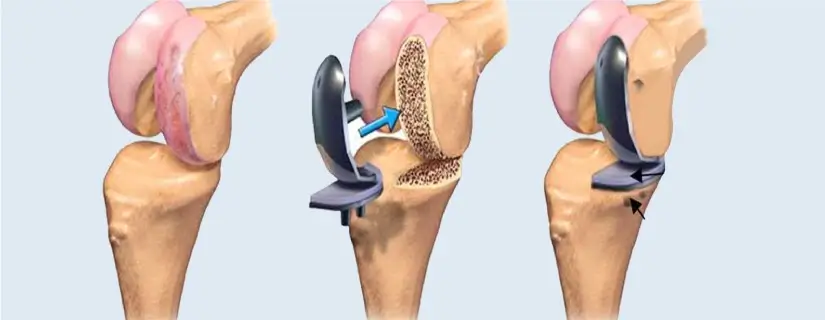
1. Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
Total knee replacement removes damaged cartilage and bone from the knee joint and replaces them with artificial components. This surgery helps patients experiencing advanced arthritis or joint wear. It often improves walking ability and reduces chronic stiffness. TKR remains one of the most frequently performed procedures under Joint replacement in India because knee-related issues are widespread among adults and older individuals.
2. Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee replacement is suitable for patients with damage limited to one section of the knee joint. The approach preserves healthy tissue and may support quicker recovery. It is often recommended when the disease has not progressed to the entire knee structure. Patients usually experience improved movement with a smaller surgical area.
3. Total Hip Replacement (THR)
Total hip replacement replaces both the ball and socket of the hip joint. Individuals with severe arthritis, injury, or significant degeneration often choose this procedure. The artificial joint aims to restore balance and reduce pain during daily movement. THR is another common option within Joint replacement in India, as hip conditions can affect mobility and independence.
4. Partial Hip Replacement (Hemiarthroplasty)
Partial hip replacement replaces the ball portion of the joint while preserving the natural socket. It is often performed for hip fractures or localised damage. The choice depends on the patient’s age, activity level, and overall joint condition.
5. Shoulder Joint Replacement
Shoulder replacement involves replacing the damaged parts of the shoulder joint with artificial components. It helps those with severe arthritis, persistent pain, or movement restrictions. Surgeons may perform total or partial replacement depending on how much of the shoulder is affected.
6. Elbow Joint Replacement
This surgery is less common but still important to include. Elbow replacement replaces the damaged parts of the joint with artificial components to improve bending and lifting. It is typically suggested for patients with rheumatoid arthritis or complex fractures that limit daily activities.
7. Small Joint Replacements (Ankle, Wrist, Finger Joints)
Small joint replacements restore function in joints that are difficult to treat through other procedures. These surgeries help patients with advanced arthritis, traumatic injuries, or severe stiffness. Although less common than hip or knee replacements, they play a significant role for those with localised joint issues.
What Influences the Choice of Surgery
Surgeons choose the right procedure after assessing mobility, pain levels, age, lifestyle, and overall health. Imaging tests and clinical evaluations guide the final decision. Each surgery aims to provide relief while maintaining long-term joint stability.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Joint Replacement
Recovery includes physiotherapy, movement exercises, and regular follow-ups. Most patients notice an improvement in mobility after completing their rehabilitation plan. The goal is to regain strength and use the new joint safely and confidently. The duration of recovery varies based on the joint replaced and the individual’s health.
Conclusion
Joint replacement has become a dependable option for patients with long-term pain, reduced mobility, or damaged joints that no longer respond to conservative treatments. With a range of surgical options now available, individuals can receive targeted care based on the specific joint affected. Knee and hip procedures remain the most common choices in joint replacement in India, while shoulder, elbow, and small-joint surgeries also support those with localised problems. A precise diagnosis and a structured treatment plan help patients make informed decisions. Joint replacement continues to play a vital role in restoring comfort, movement, and independence for many individuals across the country.